Cardiac output is the measurement of blood flow from the heart through the ventricles, and is usually measured in liters per minute. Any factor that causes cardiac output to increase, by elevating heart rate or stroke volume or both, will elevate blood pressure and promote blood flow. Sinus rhythm is the normal regular rhythm of the heart set by the natural pacemaker of the heart called the sinoatrial node. It is located in the wall of the right atrium. Normal cardiac impulses start there and are transmitted to the atria and down to the ventricles.
Flow Chart Upon Immediate Standing Of Cardiac Rate
Cardiovascular physiology is the study of the cardiovascular system, specifically addressing the physiology of the heart ('cardio') and blood vessels ('vascular').
These subjects are sometimes addressed separately, under the names cardiac physiology and circulatory physiology.[1]
Although the different aspects of cardiovascular physiology are closely interrelated, the subject is still usually divided into several subtopics.
- 2Regulation of blood pressure
Heart[edit]
- Cardiac output (= heart rate * stroke volume. Can also be calculated with Fick principle.)
- Stroke volume (= end-diastolic volume − end-systolic volume)
- Ejection fraction (= stroke volume / end-diastolic volume)
- Cardiac output is mathematically ` to systole[clarification needed]
- Inotropic, chronotropic, and dromotropic states
- Cardiac input (= heart rate * suction volume Can be calculated by inverting terms in Fick principle)
- Suction volume (= end-systolic volume + end-diastolic volume)
- Injection fraction (=suction volume / end-systolic volume)
- Cardiac input is mathematically ` to diastole[clarification needed]
- Electrical conduction system of the heart
Regulation of blood pressure[edit]
- Renin–angiotensin system
- Aortic body and carotid body
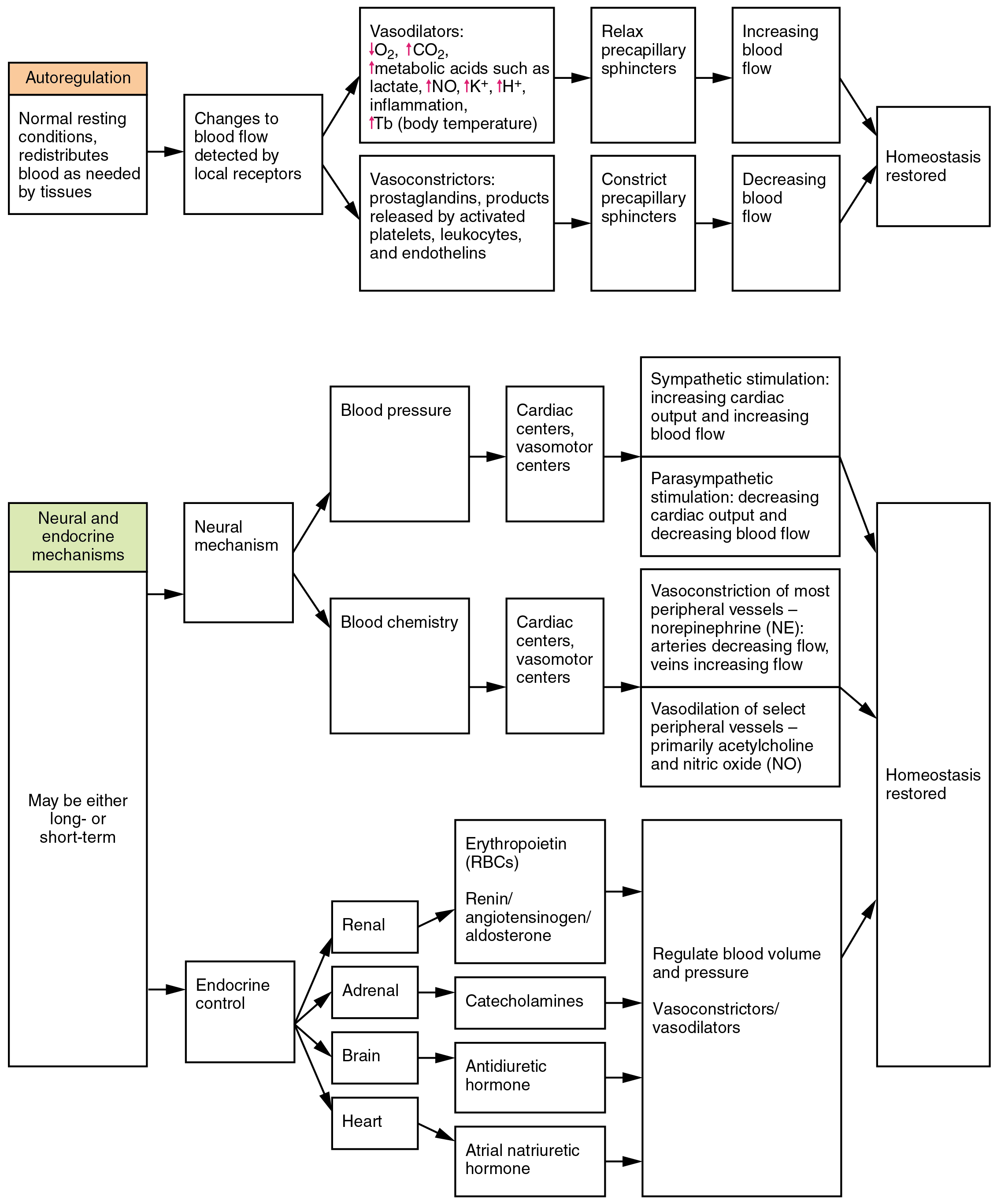
- Autoregulation

Hemodynamics[edit]
Under most circumstances, the body attempts to maintain a steady mean arterial pressure.
When there is a major and immediate decrease (such as that due to hemorrhage or standing up), the body can increase the following:
- Total peripheral resistance (primarily due to vasoconstriction of arteries)
Adobe acrobat x pro upgrade. In turn, this can have a significant impact upon several other variables:
- Pressure
- Pulse pressure (systolic pressure - diastolic pressure)
- Mean arterial pressure (usually approximated with diastolic pressure + 1/3 pulse pressure)
Regional circulation[edit]

| Name of circulation | % of cardiac output | Autoregulation | Perfusion | Comments |
| pulmonary circulation | 100% (deoxygenated) | Vasoconstriction in response to hypoxia | ||
| cerebral circulation | 15%[2] | high | under-perfused | Fixed volume means intolerance of high pressure. Minimal ability to use anaerobic respiration |
| coronary circulation | 5% | high | under-perfused | Minimal ability to use anaerobic respiration. Blood flow through the left coronary artery is at a maximum during diastole (in contrast to the rest of systemic circulation, which has a maximum blood flow during systole.) |
| splanchnic circulation | 15% | low | Flow increases during digestion. | |
| hepatic circulation | 15% | Part of portal venous system, so oncotic pressure is very low | ||
| renal circulation | 25% | high | over-perfused | Maintains glomerular filtration rate |
| skeletal muscular circulation | 17%[3] | Perfusion increases dramatically during exercise. | ||
| cutaneous circulation | 2%[4] | over-perfused | Crucial in thermoregulation. Significant ability to use anaerobic respiration |
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^OverviewArchived January 17, 2007, at the Wayback Machine at Medical College of Georgia
- ^Essentials of Human Physiology by Thomas M. Nosek. Section 3/3ch11/s3c11_13.
- ^Essentials of Human Physiology by Thomas M. Nosek. Section 3/3ch11/s3c11_2.
- ^Essentials of Human Physiology by Thomas M. Nosek. Section 3/3ch11/s3c11_10.
External links[edit]
- Cardiovascular+physiology at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Cardiovascular Physiology Concepts - Comprehensive explanation of basic cardiovascular concepts, based on a textbook of the same name.
- The Gross Physiology of the Cardiovascular System - Mechanical overview of cardiovascular function. Free eBook and video resources.
- Clinical Sciences - Cardiovascular An iPhone app covering detailed cardiovascular physiology and anatomy